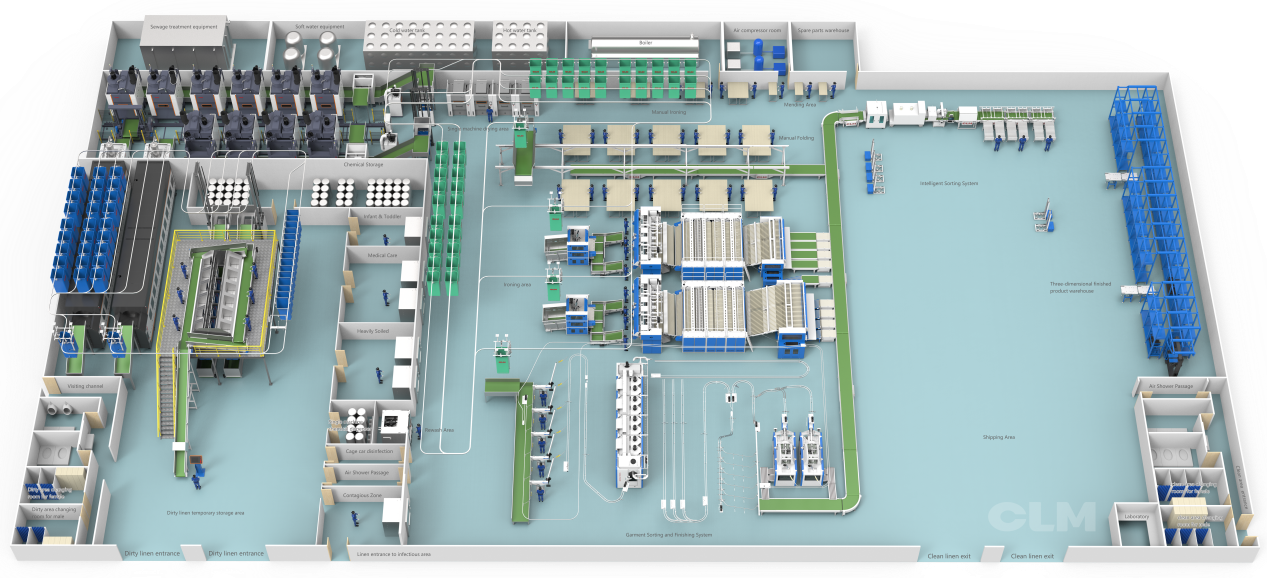
Medical linen laundry is related to both hospital staff and patients. The core task of a medical laundry plant is the prevention of cross-contamination during the whole process (washing, picking up, and delivering). The linens needed to be washed include patients’ clothes, bed sheets, surgical towels, medical staff uniforms, and more. All patients are not only carriers of pathogens (bacteria/viruses) but also potential victims of infection. Therefore, proper safety control in medical linen laundry and thorough prevention of cross-contamination are crucial for safeguarding the safety of the medical environment.
Source Control
The cross-contamination prevention should first start from the source. Before leaving the hospital, the linens should be strictly sorted and isolated according to different types:
· patients with infectious diseases and non-infected patients.
· medical staff and patients.
· infants, children, and adults.
Separate and classified isolation packaging should be adopted to isolate the linen and undergo sterilization treatment. Soiled linen should be stored separately and sent to the laundry plants quickly to reduce the opportunities for the growth and spread of pathogenic microorganisms.
Washing Process
● Secondary sorting and isolated washing
After laundry plants receive the linens, staff in laundry plants should further refine the sorting on the basis of the sorting in hospitals to avoid cross-contamination caused by mixed washing of different types of linens: linen texture, color, stain types (blood, medicine), and degree of dirt.
● Logistics and isolated space
During the laundry process, staff should strictly follow the principle of “separating clean and dirty areas” in logistics to achieve a hygienic isolation laundry mode.
All textiles must flow in one direction. The path from the area for dirty clothes to the clean area is irreversible. This helps completely eliminate the cross-infection source of dirty clothes.
Also, physical partitions can prevent air from flowing from the area for dirty clothes to the clean area. As a result, used laundry equipment should be barrier-type. The dirty clothes enter the front door, and clean clothes come out through the back door. The middle part should be completely isolated by a wall to form a physical barrier.
● Workflow and operation division
Laundry plants should clearly divide the workflow and logistics channel.
The logistics route flows in one direction: washing area, drying and ironing area, folding area, and storing area for clean linens.
The operators of dirty linen and clean linen should be strictly divided to avoid cross-contact among them. This can help avoid secondary contamination of clean linen.
Disinfection
The sterilization and disinfection of medical linen should be achieved by the triple guarantees: high temperature, dry heat, and chemical disinfection.
● High-temperature washing
High-temperature washing (over 80 degrees Celsius) for 10 to 25 minutes can effectively kill most pathogenic microorganisms.
● Dry heat disinfection
After high-temperature washing, using high-temperature drying and a dry heat environment caused by ironing can further sterilize the linens. It can also ensure the dry status of the linen and avoid dampness that breeds bacteria.
● Chemical disinfection
When facing special soiled linen, it should be soaked in chlorine-containing bleach for 25 minutes to enhance the disinfection effect.
By high-temperature washing, drying, and ironing, the medical linen laundry should ensure that it meets the sterilization and disinfection standards stipulated by the Ministry of Health. After washing, there should be no dampness at the corners of the linen, which can help avoid secondary contamination.
Key Factors of Washing Quality
● Water quality
Hard water may cause linen damage:
· White clothes turn gray or yellow.
· Fibers and colors are damaged.
· Clothes become stiff.
· Minerals in hard water can catalyze bleach, reduce the strength of linen, and even cause damage.
● Refined sorting and scientific pre-wash
There are four categories:
1. Medical staff uniforms.
2. Treatment area linens.
3. General ward linens, contaminated linens (human excrement, blood stains…)
4. Infectious linens.
· During the pre-wash process, the linen should be washed in different machines according to the types. The loading volume of the washing machines should be controlled at 70% to 80%. This leaves sufficient liquid flow space to ensure uniform detergent concentration to impact the linen and remove dirt.
When facing protein-based stains like bloodstains, adopting the low-temperature pre-wash with a low water level can avoid the yellowness or blackness of the linen caused by the dry stains or high-temperature washing and ensure the washing quality.
Conclusion
Medical linen laundry plants should incorporate cross-infection prevention and control throughout the entire process. (reception, sorting, washing, sterilization, and disinfection). Strictly controlling the water quality, obeying the operation standards, and sterilization standards can provide reliable linen laundry service for the medical institutions and help safeguard the safety of the hospital staff and the patients.
Post time: Oct-10-2025